The Solar Equinoxes And Solstices Are Computed According To The Following Astronomical Definitions Using Solar Coordinates Computed By The VSOP87 Theory, Series C,
And Refined With IAU Nutation Series 2000B.
Applied Definition Of Equinox
There are two equinoxes each year marking the dates on which the spring and autumn seasons begin and the apparent geocentric sun crosses the celestial equator. The term "equinox" derives from Latin for "equal nights" and refers to those dates of the year when the days and nights throughout the world are most closely equal in length (closer to 12h/12h) than on any other dates of the year.
In astronomical terms, the equinoxes occur twice each year at the moment the sun reaches apparent geocentric equatorial declination 0 (zero) degrees.
Applied Definition Of Solstice
There are also two solstices which mark the dates on which the summer/winter seasons begin and which also mark the longest days/nights of the year. The term "solstice" is related to sol=sun and stasis=motionless or standing still, so-named because these are the dates when the sun appears to reach its highest or lowest midday altitude in the sky and appears to hover at that altitude (in solar stasis) for a day or so before slowing starting to move back in the opposite direction, southward or northward, depending on the season, a little more each day.
In astronomical terms, the solstices occur twice each year, the first in June at the moment when the sun reaches the apparent geocentric equatorial right ascension of 6 hours or 90 degrees and again in December, when the right ascension reaches 18 hours or 270 degrees.
The Eight Seasons Of The Year
There are eight distinct seasons on Earth each year. Both the northern and southern hemisphere each experience the same four seasons, but at opposite times of the year, which adds up to eight distinct seasons per year, around the world. For example, when it is summer in New York City, USA, it is winter in Melbourne, Australia and vice versa. Since their respective seasons all occur at opposite times of the same year, it constitutes two distinct occurrences of each season or eight distinct seasons each year.
Let: BLUE Seasons = Northern hemisphere and RED Seasons = Southern hemisphere
- March - Spring / Autumn - Equinox
Begins at the moment when the apparent geocentric sun reaches declination = 0°
and crosses the celestial equator from south to north.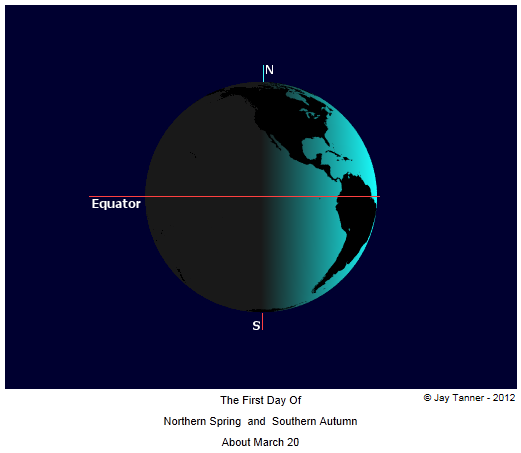
- June - Summer / Winter - Solstice
Begins at the moment when the apparent geocentric sun reaches RA = 06h (90°).
Sun appears stationary at northernmost declination (approx.+23.45°), before heading
back south a little more each day.
- September - Autumn / Spring - Equinox
Begins at the moment when the apparent geocentric sun reaches declination = 0°
and crosses the celestial equator from north to south.
- December - Winter / Summer - Solstice
Begins at the moment when the apparent geocentric sun reaches RA = 18h (270°).
Sun appears stationary at southernmost declination (approx.-23.45°), before heading
back north a little more each day.
USNO-Ref: http://aa.usno.navy.mil/data/docs/EarthSeasons.php